Interactive LearningPythagoras
Watch the vidoe above first for everything you need to know in order to understand Pythagroas.
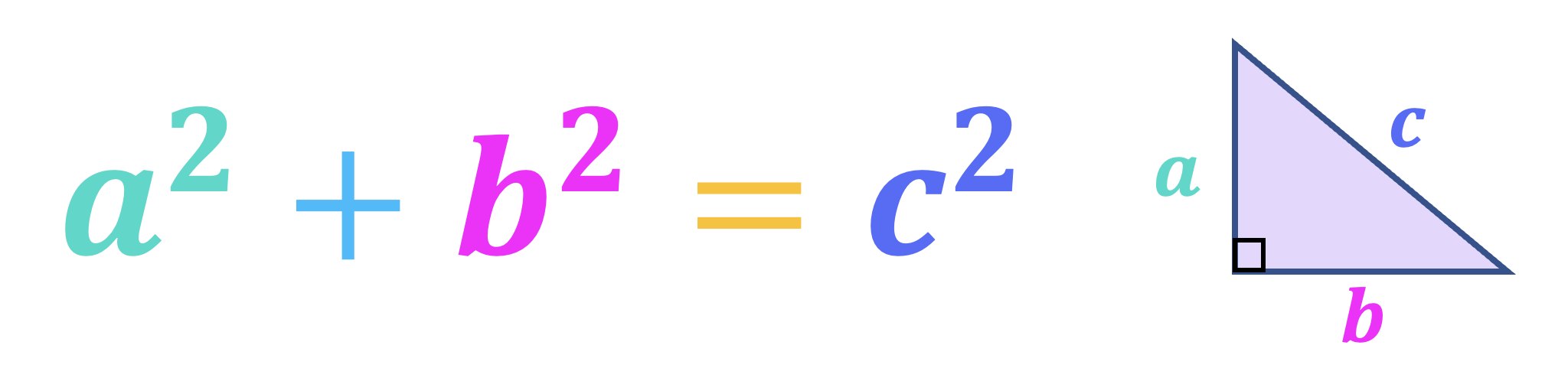
If we have a right-angled triangle, then the sum of the squares of the two smaller sides (a and b) is equal to the square of the larger side (c).
Why is this true? We can create squares on each of the three sides of the triangle and consider each of their areas.
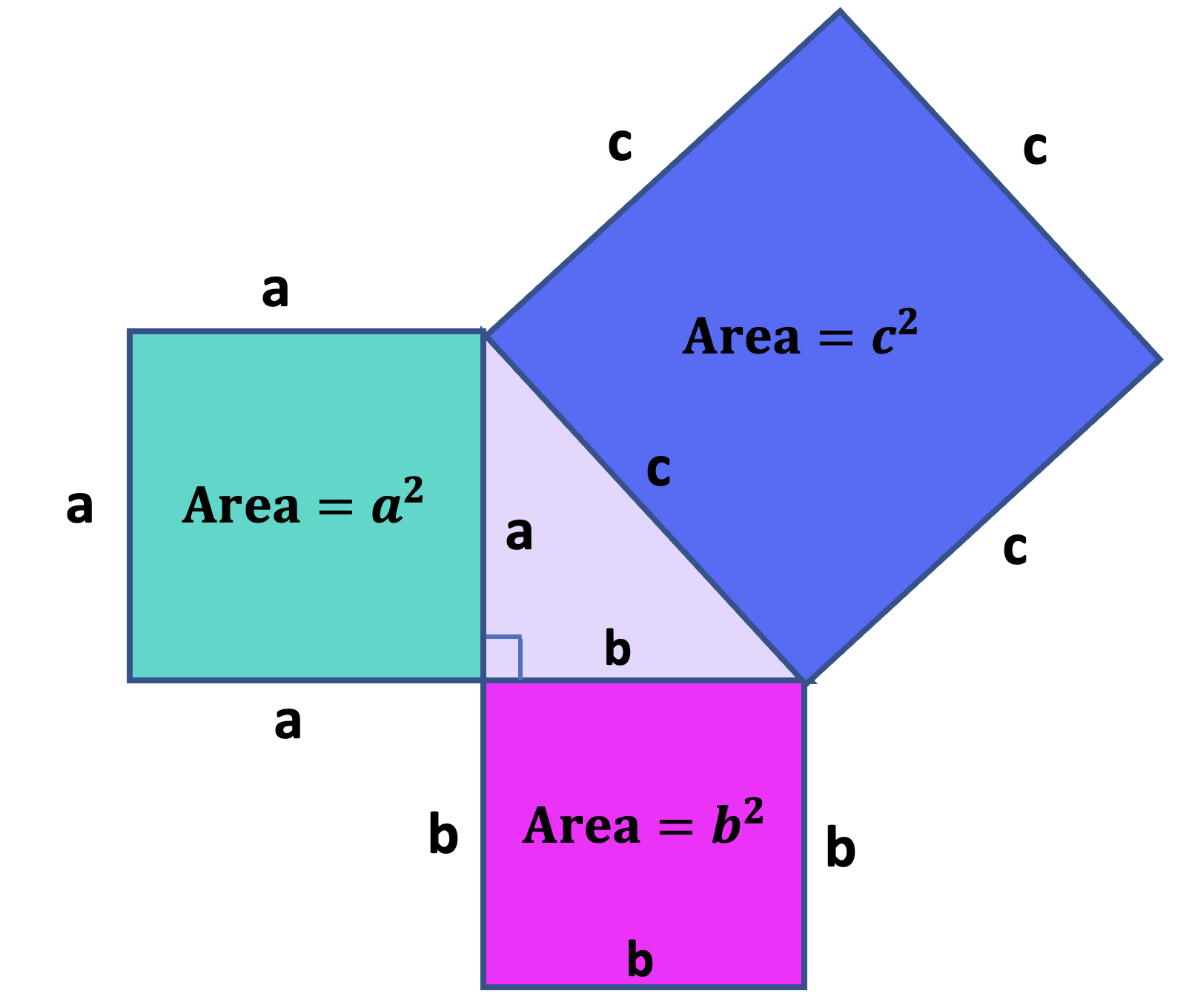
A nice visual representation
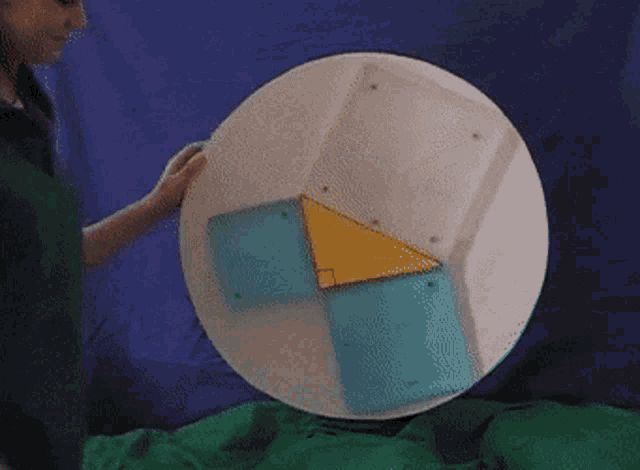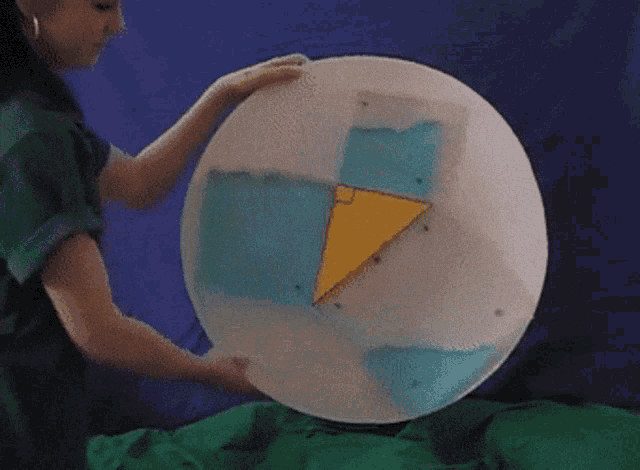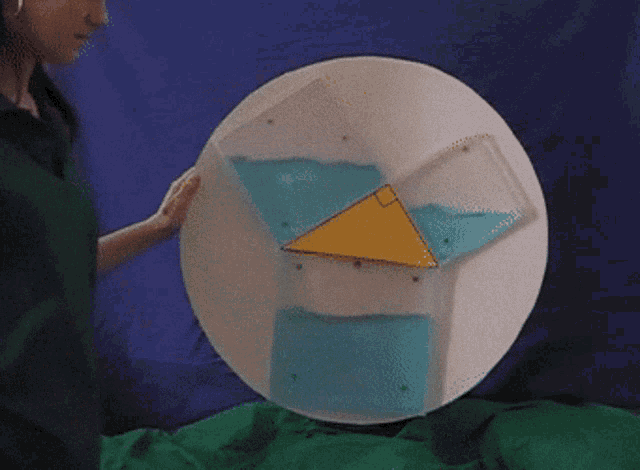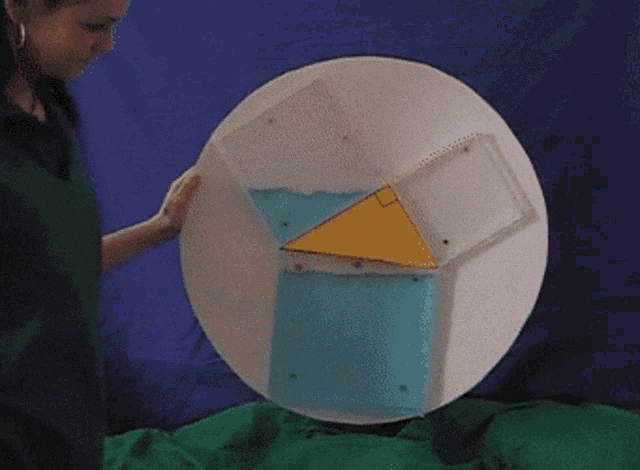

There are many ways to display the proof, depending on how we divide up the squares. Let's look at some of the possible options.
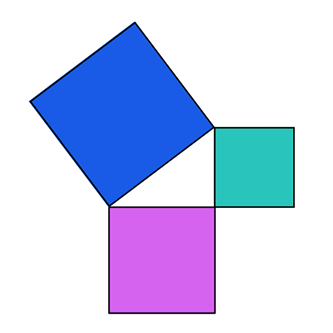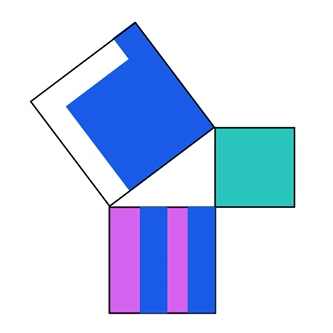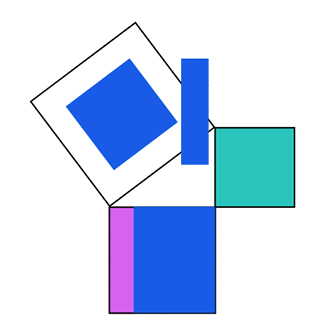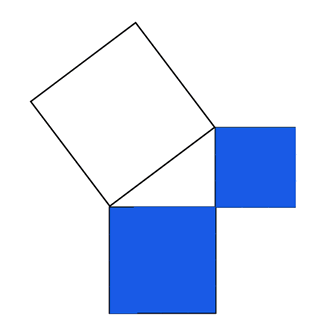
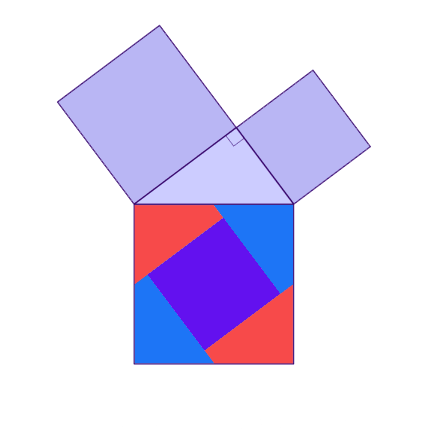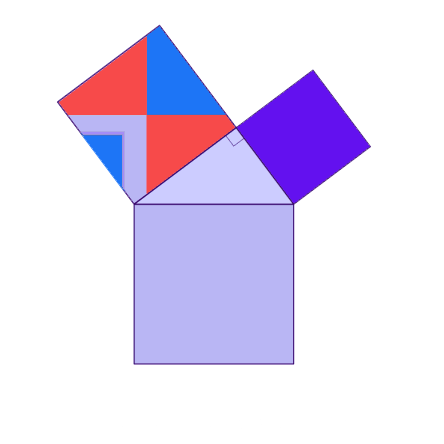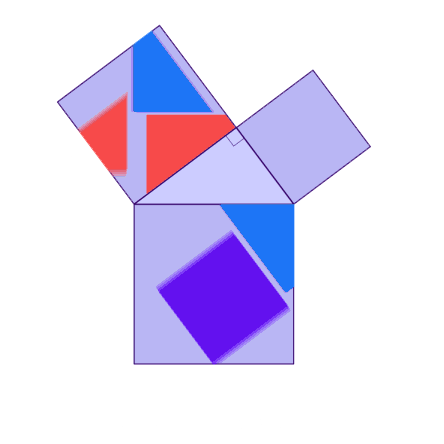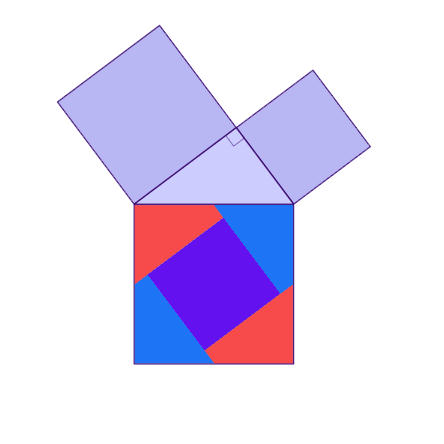
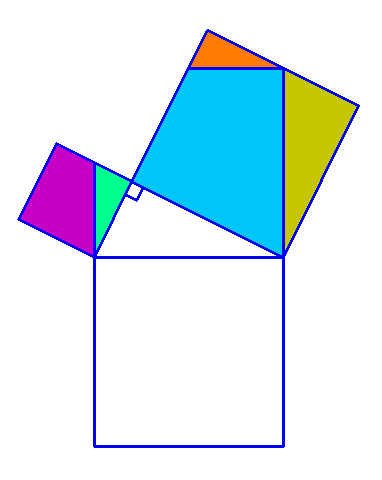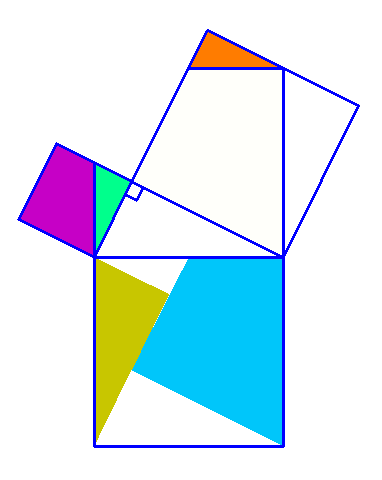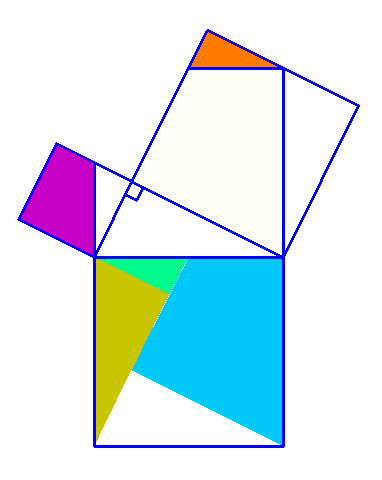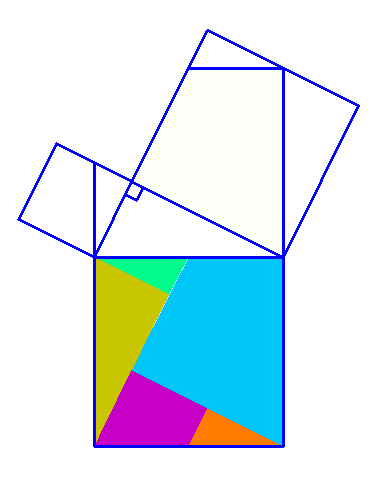
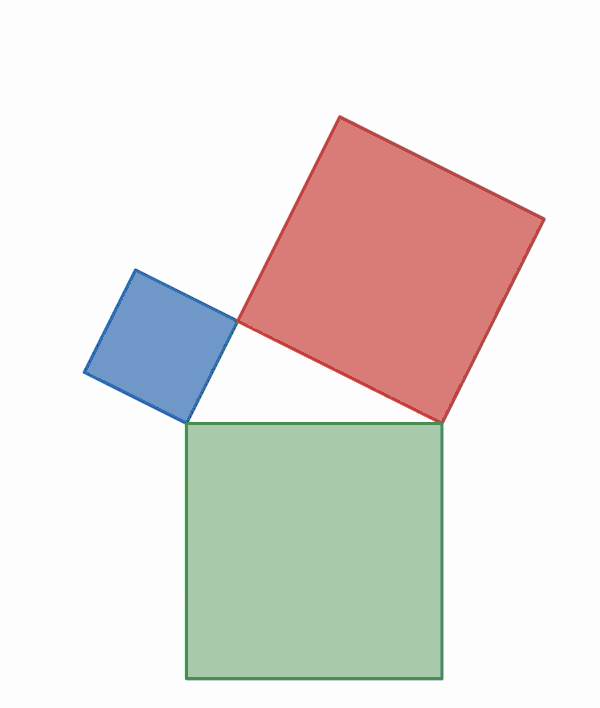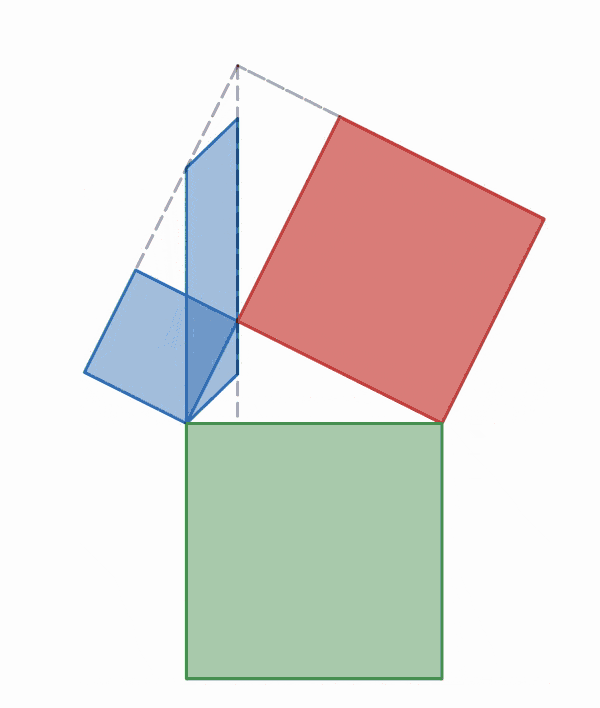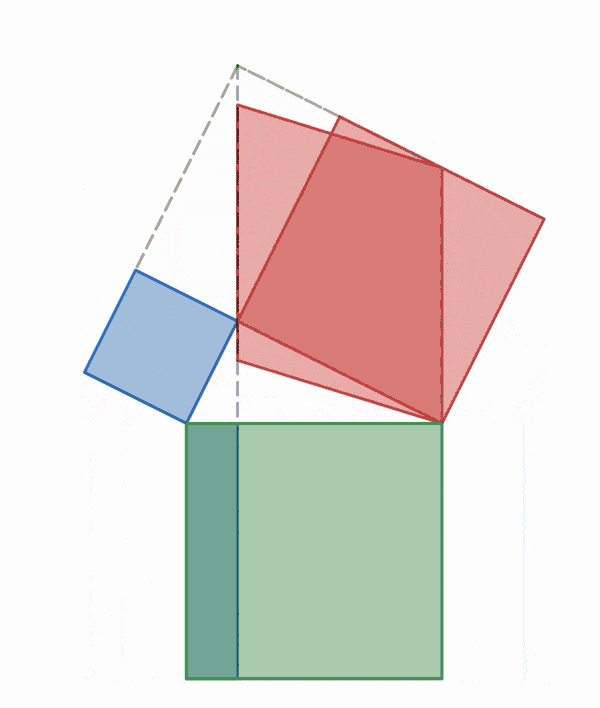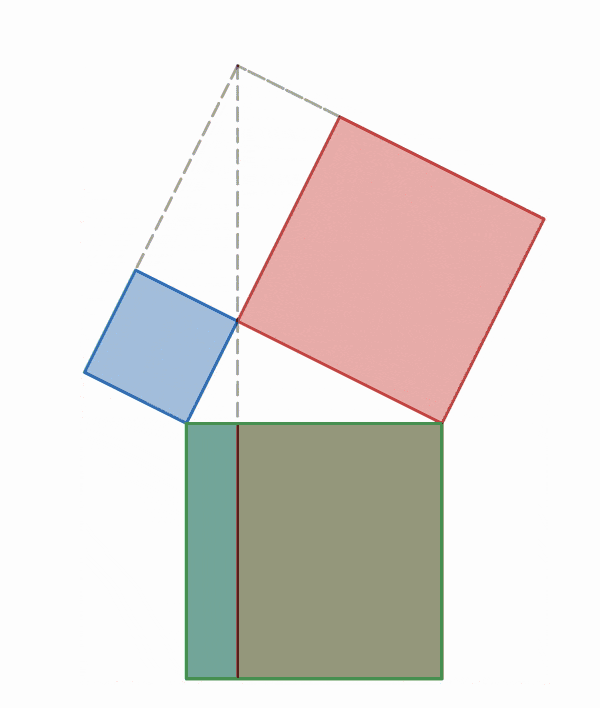
.
Fractal Pythagoras Tree:
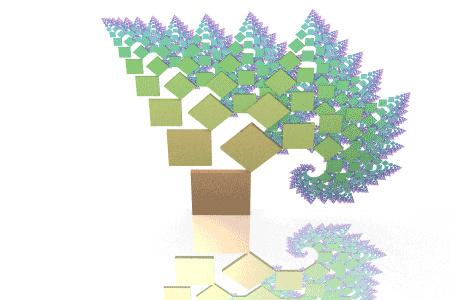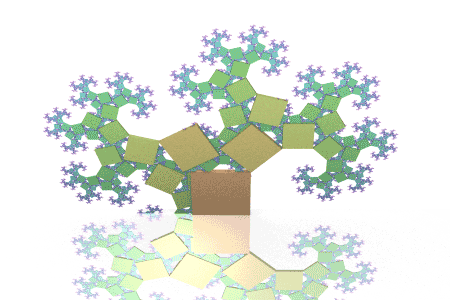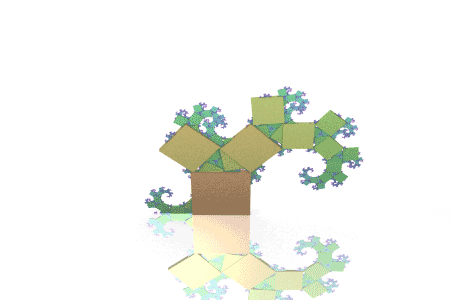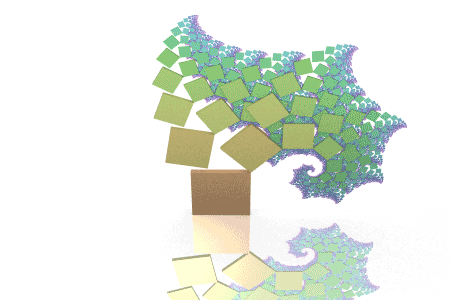
See the slides below for how to apply Pythagroas in all types of questions and the best methods to use.